In the hustle of our school semester starting, I forgot to post about possibly the most exciting app news I have heard this summer.
After writing about it and talking about it on the podcast for well over a year, I am pleased to say that forScore has announced they are making a native Mac app. It will be coming this fall, alongside their version 12 update. Read all about version 12 here...
forScore comes to the Mac in a big way with a brand new, fully native experience built for some of the most advanced and powerful devices out there. forScore runs on macOS Big Sur, both on Intel and Apple Silicon-powered Macs, and it’s included with forScore for iOS and iPadOS as a universal purchase. That’s right—it’s absolutely free for everyone who has ever bought forScore.
From the looks of it, forScore is using Apple's Catalyst technology, which allows iPad apps to be ported to the Mac.
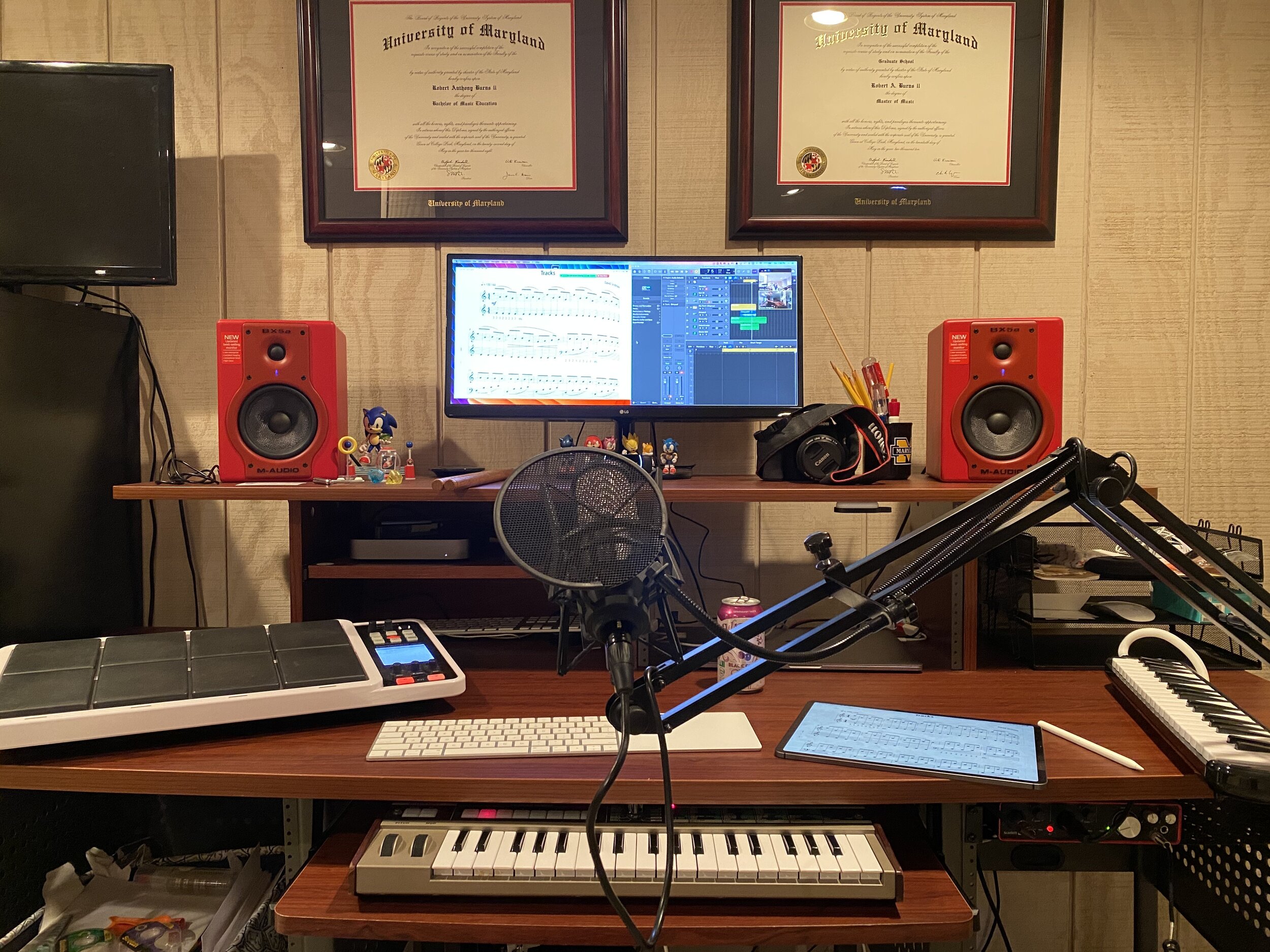
While I have not seen the Mac version of forScore, I have been testing the iOS version of forScore 12. It's great! My favorite small (but significant) feature is that you can now annotate while viewing two pages at a time without the app jolting into annotation mode. You just write directly on the screen with the Apple Pencil and your markings appear immediately.
I store my score backups on my hard drive's file system, which is how I access them on the Mac. But I store my most frequently read scores in forScore on the iPad. I am glad the experience of interacting with my sheet music will now be consistent across both devices.
Something I have felt would need to happen for this to be useful is iCloud syncing. forScore says that is coming too...
Bringing forScore to the Mac is just the beginning—a whole new platform means a whole new set of opportunities. From subtle refinements to major new features already in development like iCloud Syncing, we’re building the future one step at a time.
We’re just getting started. Again.
Using a Mac version of the app with the need to maintain two separate score libraries would have been a nonstarter for me. As an added side benefit, I can see this getting me to use forScore on the iPhone. Its not the best screen size for sheet music, but every now and then, I'd like to be able to take it out of my pocket and reference a score real quick. The problem is that it is never real quick because none of my scores are there!
I could not be more excited about this announcement!