This post first appeared on the NAfME Blog on December 7, 2021. You can read it there by clicking here.
Always Start from the Beginning
Every year I teach band, I start from the beginning. I find that if I rebuild the ensemble, focusing on fundamentals, it is impossible to fail.
This is especially true after many programs have lost over a year of in-person instruction. Even if students' skills have been sustained or improved, they are likely returning to the classroom with less handle on things that they can only learn in a group: intonation, balance, blend, and even basic rehearsal expectations.
They will have to relearn how to listen outside their comfortable bubble of one.

Caption: A mixer at the front of the room allows me to pump my voice, computer, and phone through a stereo and mix them to taste.
I want to describe some of the teaching strategies that have been most helpful this fall (and long since before COVID) while also sharing some technological tips I have taken from virtual learning into this year. I will explain how I am implementing them in my beginning band class to ensure that they develop great ears, strong ensemble sound, musicianship, and all while preparing concert music.
Developing the Ear
All excellent music-making starts with the ear. In Musical Performance: Learning Theory and Pedagogy, Daniel Kohut claims that students need a “superior concept” of the sound they wish to make. I believe this is much easier to achieve while playing in unison. Young musicians often learn this way by nature of beginning method books focusing on familiar, unison melodies, which elementary school teachers teach in instrument-specific sectionals. But when students first join a large ensemble, they can lose their independent sense of tone, intonation, and balance if too many separate voices start happening in their concert literature too soon.

Caption: The Tonal Energy Tuner app is only a few dollars, and it play justly in-tune polyphonic drones and a metronome simultaneously.
My Concert Band class has 50 6th and 7th-grade students. Many of these students are first-year players. This year, most of them had only experienced a half year of in-person band before walking into my classroom.
I decided to keep them playing in unison for as long as I could keep them interested. I wanted to emphasize tone quality, intonation, balance, and bend, while somehow managing the classroom and preparing them for a December concert. And I wanted to keep things fun. Was it possible to do all of this? Yes!

Caption: Dorico’s popovers, like this one for dynamics, allow you to enter notation naturally and quickly. Adding solfege with the Lyrics popover was equally easy.
Transforming Concert Literature into Unison Melodies
I started by ensuring that I centered instruction around accessible melodic material from the method book rather than technical exercises and drills. Additionally, I took the pieces I was planning for our winter concert and wrote out every person's part for every instrument using Dorico. Dorico’s keyboard shortcuts and flow-based composing make it easy to design supplemental resources as quickly as you can think.

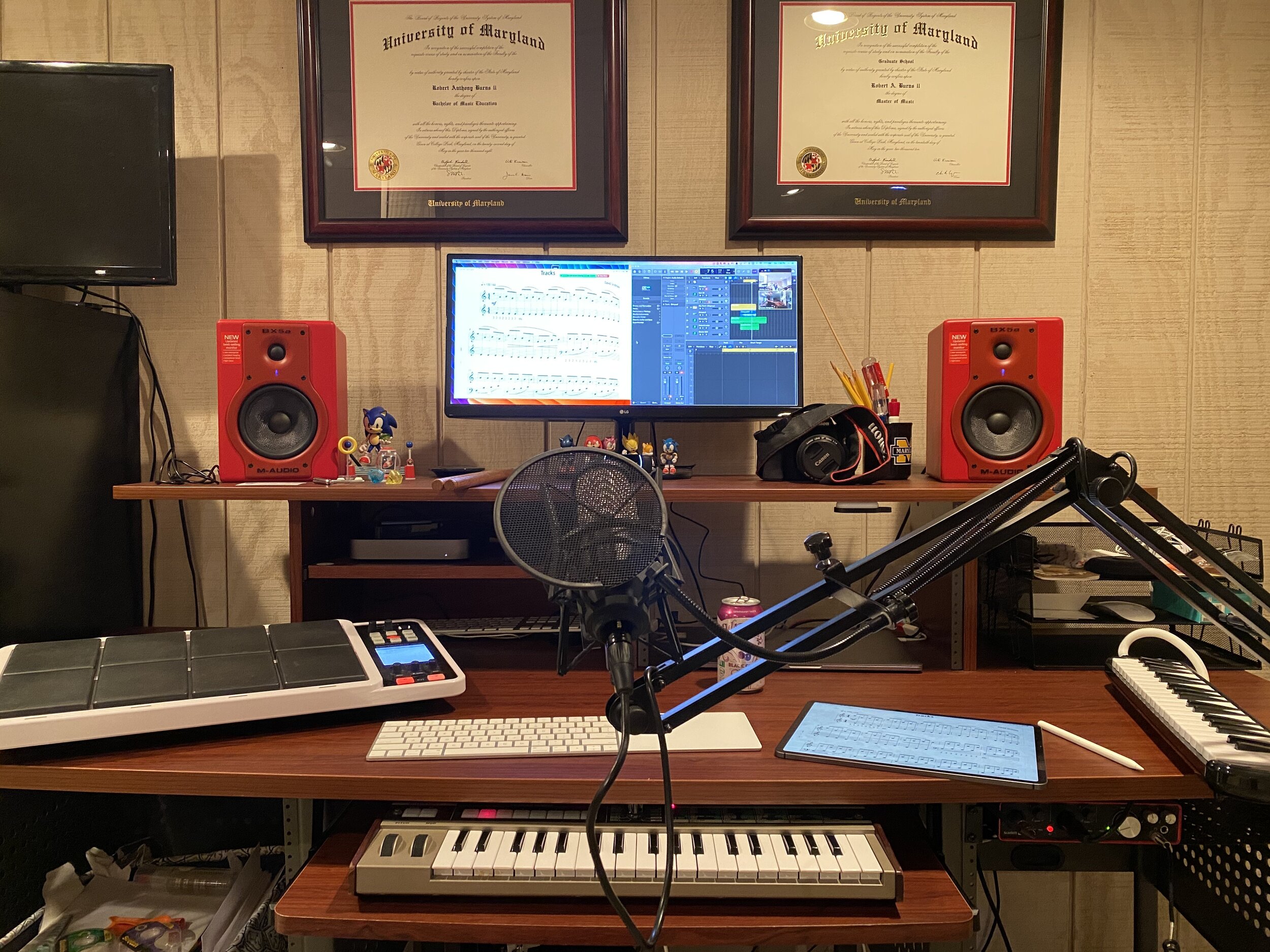
Caption: Last school year, my team purchased some equipment to support hybrid teaching. This year, we have repurposed that gear to integrate audio technology into traditional rehearsals seamlessly.
The guides are organized by rehearsal marking. For example, Part 1 has everyone in the band playing the bass line of measures 1-8. By playing each part of the music sequentially, students get more practice sight-reading while learning who in the band plays which notes. By playing in unison, they leverage their strength in numbers to develop firmer and more stable tone quality while learning to hear what an ensemble blend should sound like for the first time.

Caption: This is what an individual part looks like in Dorico once completed. Instead of isolating sections of the band during rehearsal, I can have everyone playing at all times. For example, if I want to work with the tuba part in measure one, I can tell the entire band to play “Part 1. Lower Voice” and keep everyone engaged.
I write solfege into these practice guides and alternate between the students singing and playing. In a year without any COVID concerns, I would also encourage the brass to buzz these melodies on mouthpieces to develop their inner ear and flexibility.
Play-Along Resources Help Model Tone, Intonation, and Tempo
There is always a drone prominently playing through our sound system using the Tonal Energy Tuner app. The polyphonic drones can model justly in-tune intervals. Students can subtly adjust their pitch by making the “beats” that result between two out-of-tune pitches slow down and eventually dissolve.

Caption: One of the easiest and most engaging ways to encourage metronome practice is to play along to the Drummer Tracks in GarageBand. There are numerous styles, beats, and editing tools at your disposal. Beats are way more fun to play with and provide more musical feeling than a metronome.
I have created play-along tracks that combine trap beats with tuning drones. I like to pump them through the speakers during warm-ups and throughout rehearsal. You can make these too using the free GarageBand app on iOS.
Sometimes, I will have Tonal Energy coming through my phone and the beats coming through my Mac. This allows me to mix the drone and the metronome independently, as they are plugged into two separate channels of my mixer.
Speaking Calmly, Being Everywhere
A Shure wireless microphone goes into a third channel of the mixer, allowing me to speak in a comfortable room voice and be heard over the sound of loud drones, beats, and a full band of 50-65 students playing.
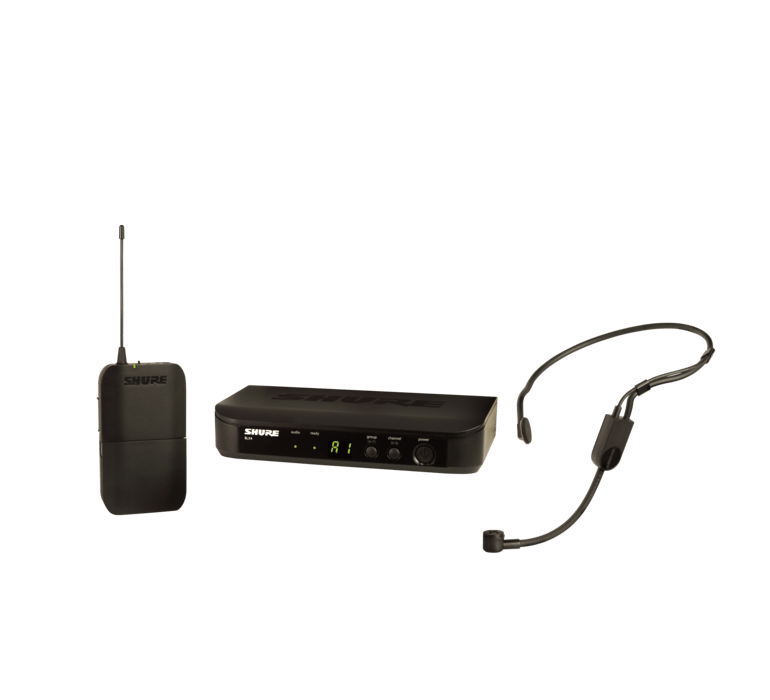

Caption: This Shure wireless headset microphone has been a game-changer this year. I don’t ever have to raise my voice to be understood. I can speak comfortably and be heard over the sound of a pumping drone and 60 students playing.
This technique works wonders for classroom management. Flowing from one part of our daily agenda to the next is nearly seamless because of how easy it is to keep everyone playing most of the rehearsal. With these persistent play-alongs underlying most of the rehearsal, my role could be described less like a traditional director and more like a spin instructor.
This might sound ridiculous at first, but it is true. A spin instructor curates music, keeps the beat moving you forward and paces instruction, all while making you sweat. This is precisely how I want my role to feel in the band room. I like to think of myself as a “coach” who directs students towards the goal while they work for it, rather than a “director” who beats the music into them.

Caption: My colleague, Ben Denne, teaches from our “command station” at the front of the room.
The wireless mic allows me to step off the podium and be heard from anywhere in the room. While the band is playing, I can be high-fiving students, sizing a student for concert attire, helping percussionists find their place, encouraging good trombone posture, or any other need. I can be everywhere and still keep the flow of rehearsal moving even when I’m off the podium.

Caption: Farrago is a useful app for queuing play-along material in a soundboard-style audio launcher. I keep my scale tracks organized and color-coded by key and rhythmic patterns to find them more easily.
Taking the Slow Road Gets Maximum Results
Once it is time to hand out concert music, I'm delighted to hear students say things like, "wait, we know this!." By this point, they can sing every part, play every part, and can now split into three or four unique voices because they are more confident in their melody from having practiced it with the strength of 60 musicians in unison.

Caption: AnyTune is another excellent app that can change the speed and pitch of a play-along track independently.
The results are clear. I have never had a more engaging, fun, and tightly managed beginning band experience. Students are developing fundamentals at a pace consistent, if not better, than a typical year, and we are stronger for it.